Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Naoe, Takashi; Xiong, Z.*; Futakawa, Masatoshi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 506, p.12 - 18, 2018/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:58.07(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)A mercury target for neutron source (made of 316L SS) suffers not only proton and neutron radiation damage, but also cyclic impact stress caused by pressure waves. In the previous study, we carried out an ultrasonic fatigue test to investigate the gigacycle fatigue strength of 316L SS, concluding that specimen surface temperature rose abruptly more than 300 C just before failure. In this study, to clarify the mechanism of the temperature rise, we measured temperature distribution with a thermography during the fatigue test. The experimental results showed that the temperature rose locally only at the crack tip and the peak position moved with the crack propagation. We also carried out a nonlinear structural analysis by LS-DYNA to estimate the temperature rise with strain energy of elements. The analytical result showed that the heat due to plastic deformation at the crack tip is dominant for the temperature rise rather than the friction between crack surface.
C just before failure. In this study, to clarify the mechanism of the temperature rise, we measured temperature distribution with a thermography during the fatigue test. The experimental results showed that the temperature rose locally only at the crack tip and the peak position moved with the crack propagation. We also carried out a nonlinear structural analysis by LS-DYNA to estimate the temperature rise with strain energy of elements. The analytical result showed that the heat due to plastic deformation at the crack tip is dominant for the temperature rise rather than the friction between crack surface.
Okajima, Satoshi; Wakai, Takashi
Nihon Kikai Gakkai 2017-Nendo Nenji Taikai Koen Rombunshu (DVD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2017/09
It was reported that the long distance travel of temperature distribution causes a new type of thermal ratcheting, even in the absence of primary stress. In this paper, based on the results of inelastic finite element analyses, we investigated saturation behavior of thermal ratcheting strain due to long range travel of temperature distribution. As a result, we revealed that the long distance travel of temperature distribution generates plastic strain distribution made maximum at the central part. Because of the shape of the generated strain distribution, the residual stress accumulates even at the central part of the region passed through the temperature distribution. In the case with excessive long traveling of temperature distribution, the region with plastic deformation extended to the surrounding region. Otherwise, sufficient magnitude of residual stress to cause shakedown behavior accumulated on entire region, and the accumulation of the plastic strain saturated.
Sato, Masayasu; Isayama, Akihiko; Inagaki, Shigeru*; Nagayama, Yoshio*; Kawahata, Kazuo*; Iwama, Naofumi*
Europhysics Conference Abstracts (CD-ROM), 29C, 4 Pages, 2005/00
no abstracts in English
Kuramochi, Masaya*; Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu
JAERI-Tech 2003-055, 148 Pages, 2003/07
The injection beam dump of the 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (3 GeV-RCS) is to be installed to absorb the H and H
and H beams that can not be changed into H
beams that can not be changed into H beam with a graphite foil. We estimate the maximum temperature and thermal stress of the injection beam dump. As a result, the temperature at the center region made of iron reached up to 370 K after several operation cycles (one cycle is three-week operation including one-week interval) under the 1kW-beam injection. Then, the temperature at the boundary between the iron region of the beam dump and the concrete wall of the tunnel was rather low temperature of about 320 K. And the maximum Mises stresses of 96 MPa and about 0.2 MPa were generated in the iron region and the concrete wall respectively. These values were much lower than the allowable temperature and stresses.
beam with a graphite foil. We estimate the maximum temperature and thermal stress of the injection beam dump. As a result, the temperature at the center region made of iron reached up to 370 K after several operation cycles (one cycle is three-week operation including one-week interval) under the 1kW-beam injection. Then, the temperature at the boundary between the iron region of the beam dump and the concrete wall of the tunnel was rather low temperature of about 320 K. And the maximum Mises stresses of 96 MPa and about 0.2 MPa were generated in the iron region and the concrete wall respectively. These values were much lower than the allowable temperature and stresses.
Kobayashi, Shinichi*; Yamano, Yasushi*; Matsukawa, Makoto
Denki Gakkai Kenkyukai Shiryo, p.79 - 84, 2001/11
no abstracts in English
Imai, Etsuya*; Shiina, Yasuaki; Hishida, Makoto*
Heat Transfer-Asian Research, 30(4), p.301 - 312, 2001/06
no abstracts in English
; kasahara, Naoto; ; ; Kamide, Hideki
JNC TN9400 2000-010, 168 Pages, 2000/02
Thermal striping is significant issue of the structural integrity, where the hot and cold fluids give high cycle fatigue to the structure through the thermal stress resulted from the time change of temperatur distibution in the structure. In the sodium cooled fast reactor, temperature change in fluid easily transfers to the structure because of the high thermal conductivity of the sodium. It means that we have to take care of thermal striping, The thermal striping is complex phenomena between the fluid and structure engineering fields. The investigations of thermal striping are not enough to evaluate the integrity directly. That is the fluctuation intensity at the structure surface is assumed to be temperature difference between source fluids (upstream to the mixing region) as the maximum value in the design. 0therwise, the design conditions are defined by using a mockup experiment and large margin of temperature fluctuation intensity. Furthermore, such evaluation manners have not yet been considered as a design rule. Transfer mechanism of temperature fluctuation from fluid to structure has been investigated by the authors on the view points of the fluid and structure. Attenuation of temperature fluctuation was recognized as a dominant factor of thermal fatigue. We have devdoped a numerical analysis system which can evaluate thermal fatigue and crack growth with consideration of the attenuation of temperature fluctuation in fluid, heat transfer, and structure. This system was applied to a real reactor and the applicability was confirmed. Further verification is planned to generalize the system. For the higher cost performance of the fast reactor, an evaluation rule is needed, which can estimate thermal loading with attenuation and can be applied to the design. An idea of the rule is proposed here. Two methods should be prepared; one is a precise evaluation method where mechanism of attenuation is modeled, and the other is simple evaluation method where ...
; ; ; ; Kamide, Hideki
JNC TN9400 2000-025, 78 Pages, 1999/11
Local blockage issue in a fuel subassembly is one of initiation of local fault in a fast reactor core. ln existing studies, it is shown that blockage in a wire-spacer type pin bundle will consist of small particles coming through the bundle and will be porous. ln order to evaluate the integrity of fuel pins covered by the porous blockage, we have to predict thermohydraulics in the blockage and also in the pin bundle. ln this study sodium experiments were carried out using a 37-pin bundle test section with a porous blockage. The fueI pins are modeled by electric heater pins of 8.5 mm in diameter (full scale). The blockage is formed by stainless steel spheres of 0.3 mm in diameter. The blockage is set in the two rows of subchannels along one side of hexagonal wrapper tube. The length of blockage in axial direction is 35 mm and corresponds to 1/6th of wire wrapping pitch. The experimental parameters were power of the heater pins. The heater power was varied from 14% to 43% of the maximum linear heat rate of a real reactor ( 420W/cm). The flow rate in the subassembly was set at 430 l/min corresponding to 93% of the Reynolds number in a fuel subassembly of real reactor under full power condition. The experimental results showed that the highest temperature was measured on the pin surface covered by the blockage and faced to the subchannel which was surrounded by the blockage. The height of peak temperature point was nearly top of the blockage. lt means that the temperature field in the blockage is influenced by flow filed in the blockage significantly. The non-dimensional temperature profile in the blockage and in the pin bundle is independent on heater power.
420W/cm). The flow rate in the subassembly was set at 430 l/min corresponding to 93% of the Reynolds number in a fuel subassembly of real reactor under full power condition. The experimental results showed that the highest temperature was measured on the pin surface covered by the blockage and faced to the subchannel which was surrounded by the blockage. The height of peak temperature point was nearly top of the blockage. lt means that the temperature field in the blockage is influenced by flow filed in the blockage significantly. The non-dimensional temperature profile in the blockage and in the pin bundle is independent on heater power.
Miura, Akihiko;
JNC TN8410 99-044, 189 Pages, 1999/10
This report includes several results that were made by calculation with several methods to clarify the cause of the fire and explosion incident. In the early times, we didn't have exact information of chemicaI property, reaction rate and any physical constants that we needed. But because the only data that indicate the cooling process of bituminized product was reported, we made heat-transporting calculation with taking this data. Based on the theory of the thermal hazard evaluation that was called Semenov theory or Frank-Kamenetskii theory, the amount of heat generation was estimated using the heat transporting calculation. Common theories were introduced in first section. In the second section, several results of heat transporting calculation were indicated. Calculations were made as follows. First, the model of bituminized product that was filled in the drum was created with the data of cooling process. Second, when the heat was generated in the drum, time-dependent temperature distribution was calculated. And last, judging from the balance of heat generation and heat radiation the critical heat rate was estimated.
Imai, Etsuya*; Shiina, Yasuaki; Hishida, Makoto*
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu, B, 65(634), p.227 - 233, 1999/06
no abstracts in English
Isayama, Akihiko; Isei, Nobuaki; Ishida, Shinichi; Sato, Masayasu; *; *
JAERI-Research 99-021, 34 Pages, 1999/03
no abstracts in English
Oba, Hironori; Shibata, Takemasa
JAERI-Research 98-069, 20 Pages, 1998/11
no abstracts in English
Yamauchi, Toshihiko; Hoshino, Katsumichi; Kawashima, Hisato; Ogawa, Toshihide; Kawakami, Tomohide; ; *
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 1, 37(10), p.5735 - 5741, 1998/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:18.91(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Sato, Masayasu; Isei, Nobuaki; Ishida, Shinichi; Isayama, Akihiko
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 67(9), p.3090 - 3099, 1998/09
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:60.62(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Okamoto, Yoshizo*; *;
Hikari Araiansu, 9(5), p.35 - 40, 1998/05
no abstracts in English
PNC TN9410 98-013, 48 Pages, 1998/03
Thermal striping phenomena characterized by stationary random temperature fluctuation are observed in the region immediately above the core exit of liquid-metal-cooled fast breeder reactors (LMFBRs) due to the interactions of cold sodium flowing out of a control rod (C/R) assembly and hot sodium flowing out of adjacent fuel assemblies (F/As). Therefore the in-vessel components located in the core outlet region, such as upper core structure (UCS), flow guide tube, C/R upper guide tube, etc., must be protected against the stationary random thermal process which might induce high-cycle fatigue. In this study, frequency characteristics of stationary random temperature fluctuations were investigated by the use of the time-series data from parallel impinging jet experiments, TIFFSS-I. From the investigations, the following results have been obtained; [Auto-Power Spectral Density Functions] (1)Higher frequency componets were decreased drastically with the close to the test piece surface, due to the presence of filtering effect by the laminar sub-layer and heat tansfer to the surface from coolant. (2)Dependence to the nozzle velocities was observed at the outside and inside positions of the laminar sub-layer region. It was due to the increasing of turbulent intensities with increase of the nozzle velocities. [Coherence Functions] (1)Coherency between outer temperatures of the laminar sub-layer was very small. 0ne of the main reasons is that the outer temperatures of the laminar sub-1ayer were dominated by the stationary random phenomena of turbulence flows. (2)It was confirmed that the coherency between immediate positions of different thermocouples had relatively higher values. [Transfer Functions] (1)The dominant frequency band of the gain was about 3 - 10 Hz for the transfer functions of the outer position to the inner position of the laminar sub-layer, and of the inner position of the laminar sub-layer to the test piece surface. (2)There wasno dependence of ...
PNC TN9410 98-007, 93 Pages, 1998/02
This report presents numeical results on thermal striping charactelistics at a tee junction of LMFBR coolant pipe, carried out using a direct numerical simulation code DINUS-3. In the numerical investigations, it was considered a tee junction system consisted of a main pipe (1.33 cm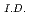 ) with a 90
) with a 90 elbow and a branch pipe having same inner diameter to the main pipe, and five velocity ratio conditions between both the pipes, i,e., (V
elbow and a branch pipe having same inner diameter to the main pipe, and five velocity ratio conditions between both the pipes, i,e., (V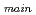 / V
/ V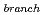 ) = 0.25; 0.5; 1.0; 2.0 and 4.0. From the numerical investigations, the following characteristics were obtained: (1)Temperature fluctuations in the downstream region of the tee junction were formulated by lower frequency components (< 7.0Hz) due to the iteractions between main pipe flows and jet flows from the branch pipe, and higher frequency components (> 10.0 Hz) generated by the vortex released frequency from the outer edge of the branch pipe jet flows. (2)On the top plane of the main pipe, peak values of the temperature fluctuation amplitude was decreased with increasing flow velocity in the main pipe, and its position was shifted to downstream direction of the main pipe by the increase of the main pipe flow velocity. (3)On the bottom plane of the main pipe, contrary to (2), peak values of the temperature fluctuation amplitude was increased with increasing flow velocity in the main pipe.
) = 0.25; 0.5; 1.0; 2.0 and 4.0. From the numerical investigations, the following characteristics were obtained: (1)Temperature fluctuations in the downstream region of the tee junction were formulated by lower frequency components (< 7.0Hz) due to the iteractions between main pipe flows and jet flows from the branch pipe, and higher frequency components (> 10.0 Hz) generated by the vortex released frequency from the outer edge of the branch pipe jet flows. (2)On the top plane of the main pipe, peak values of the temperature fluctuation amplitude was decreased with increasing flow velocity in the main pipe, and its position was shifted to downstream direction of the main pipe by the increase of the main pipe flow velocity. (3)On the bottom plane of the main pipe, contrary to (2), peak values of the temperature fluctuation amplitude was increased with increasing flow velocity in the main pipe.